Food, Beverages and Tobacco Global Industry Overview
This report analyses the global food, beverages and tobacco industry, which includes the core categories listed above.
Unless otherwise noted, all values expressed in this report are in US dollar terms, using year-on-year exchange rates.
All forecast data is expressed in current terms. The historic period refers to 2017-2022; the forecast period is 2022-2027.
Key findings
High costs still weigh on producers despite inflation slowdown in 2023
Despite an inflation slowdown in 2023, manufacturers are still impacted by the lagging effects of the uncertain economic conditions since the start of the pandemic, and especially in 2022. High energy prices, ongoing labour shortages, increase in the price of raw materials and sluggish demand due to the cost-of-living crisis have led to many companies exiting the industry, or moving to mergers and acquisitions and consolidation in order to weather the situation.
Health and wellness trends continue to drive innovation and attract consumer demand
The challenging situation during the pandemic has also opened many doors and opportunities for manufacturers to respond to rising health and environmental concerns, increase the value of their production and drive innovation. In Western countries, there has been an increase in the number of start-ups and companies looking at using technologies to increase the quality and functionality of food, beverages and tobacco products.
Geopolitical tensions lead to supply chain changes and shifting trade patterns
Rising geopolitical tensions stemming from the war in Ukraine and deteriorating relations between China and the West have caused a rearrangement of supply chains, with Russia and China turning to alternative countries in order to source their supply, decrease their reliance on Western countries, as well as boost their domestic production. This change in trade patterns has boosted the competitive advantage of countries such as Brazil and India.
Developing countries are boosting investment and government support towards food and beverage processing industries
Developing countries such as India and Indonesia are increasingly investing in their food and beverages processing capacity in order to boost their self-sufficiency, as well as increase the value of their production. With an abundance of raw materials, governments are heavily investing in machinery and inputs in order to build their production capacity, and boost the quality and safety of their products, in order to make them competitive.
Global overview
Food, beverages and tobacco industry is seeing a slowdown due to high costs
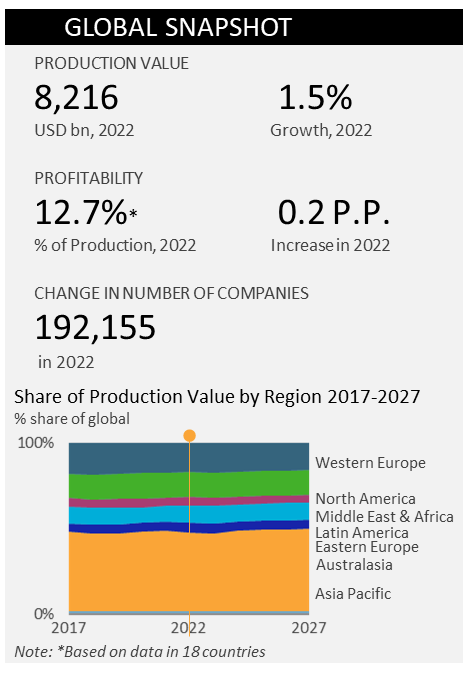
After a strong post-pandemic recovery of the production value of the food, beverages and tobacco industry in 2021, growth dropped to 1.5% in 2022, mainly hampered by strong inflationary pressure, ongoing supply chain shortages and high input costs. The food industry, in particular, was the hardest hit, due to the onset of the war in Ukraine in 2022 which led to skyrocketing energy prices and strengthened geopolitical tensions that put a strain on trade relations. Furthermore, increased labour shortages, and therefore costs, further increased costs for producers and negatively impacted the growth of the industry. The inflationary pressures have continued into 2023, and have caused consumers to shift their shopping patterns, trade down and trade off certain products.
China dominates the industry, despite strong growth of Asian countries
The production value of food, beverages and tobacco is highly concentrated in China and the US, which accounted for 40.6% of global production value in 2022. China remains the largest food producer, however slow post-pandemic economic recovery in 2023 and slow domestic demand have caused producers to suffer losses and for some companies to exit the Chinese market altogether. Nevertheless, as China is on the quest for food security, it will continue to fuel efforts towards making sure it is the dominant food producer in the world.
Furthermore, a shift towards alternative supply chains away from China, is causing other notable countries, such Vietnam, Indonesia and India to grow strongly in food production. For example, in 2022, Vietnam was the fastest growing food producer in the world, as the country is quickly becoming a key player in global agriculture, due to strong government incentives, increasing cooperation through free trade agreements and foreign investment, which is also stimulating the growth of the food and beverages processing industry. Especially due to the disruptions in China resulting from prolonged COVID-19 measures, more international companies have decided to move their operations to Vietnam and take advantage of lower costs.
Growth of the processing industry boosts costs for developing countries in 2022
2023 saw a drastic increase in industry costs due to inflationary pressures and growing labour costs. Developed countries such as the US have been particularly affected by low-skilled labour shortages and rising labour costs. Despite such countries strongly relying on automation and technology, they are still struggling with sourcing and retaining workers, which has led to a boost in technology investment, further dragging costs upwards.
Other developing countries such as Brazil, India and Indonesia have seen notable growth in their food and beverages production capacity due to a progressive move from agriculture to added-value production, which accounts for the associated growth in industry costs.
In other cases, such as in Japan, industry costs declined mainly due to a fall in B2B costs, resulting from lower operating costs and Japan’s competitive advantage against rival countries in the region. In addition, the average labour costs in agriculture decreased in comparison to the manufacturing sector, which also explains the fall in industry costs.
Inflation and added value through functionality and health drive profits in 2022
Primarily driven by inflationary pressures and trade rearrangements driven by geopolitical developments, the food and beverages industry has entered into a new phase of higher prices. With companies investing in and moving operations in developing countries due to proximity to raw materials and lower costs, countries such as Indonesia and India have seen a strong increase in profits, as the industry is in its nascent stage. However, developed countries such as Germany have seen their profits stagnate or decline, despite support from national governments, mainly due to lower productivity, stagnating economic environment and the cost-of-living crisis, which has boosted demand for cheaper products such as private label, due to their perceived quality and competitive price.
EU countries struggling with exports due to rising production costs and emissions reductions
The US is the largest exporter of food, drinks and tobacco in the world, accounting for 7.6% of global food, beverages and tobacco exports in 2022. The United States-Mexico-Canada (USMCA) free trade agreement, which entered into force in 2020, has allowed the US to export higher-value-added products to neighbouring countries and keep its leading position globally.
Germany remained the second largest food and beverages exporter in 2022, but the processing industry has begun to see a slowdown due to high energy costs resulting from the war in Ukraine, which has put a strain on the German economy. Other EU countries have also seen their export sector struggle. For example, as part of its national efforts to reduce carbon emissions, the Dutch government’s plan to buy and close thousands of livestock farms in 2022/ 2023 has caused a drop in exports of processed meat and proteins and decrease in its competitive advantage.
US and China continue to be the largest importers of food, beverages and tobacco
The US remained the largest importer of food, beverages and tobacco products in 2022, mainly due to the cultural diversity of its population, as well as the demand for variety, quality and convenience which has led to demand for more ethnically diverse products.
China has remained the second largest importer of food and beverages due to the size of its population and a rising middle class which has led to higher demand for packaged foods. Nevertheless, as China is actively looking to boost its food security, in light of rising geopolitical tensions with the West, the country has started diversifying its import sources, shifting towards more regional cooperation, as well as trade deals with BRICS countries, in addition to boosting its internal production.
The UK has also increased its imports in 2022 primarily due to Brexit and the negative impact on labour shortages and production. It has focused on negotiating new trade deals, such as with Australia in 2023 regarding imports of processed meat.
Key trends
Energy costs, labour shortages, supply chain disruptions and infrastructure hurdles continue to negatively impact the industry, despite a slowdown in inflation
Growing protectionism, trade wars and tensions, and geopolitical hurdles negatively impact the global food and beverages trade
The health and wellness trend and rising environmental concerns continue to drive investment and innovation in value-added plant-based and functional products
Macroeconomic/Industry trends
Leading companies
The top 10 food, beverages and tobacco companies see stable production value
Over the 2017-2022 period, the competitive landscape in food, beverages and tobacco has remained relatively stable and highly fragmented, with the top 10 companies accounting for 9.1% of global production value in 2022. The US company Cargill Inc remained the leading company with an increased share of 1.8%, amidst strong demand for commodities and establishment of a joint venture with Continental Grain Co to acquire Sanderson Farms, the third largest US chicken producer.
The Chinese company Cofco Corp managed to retain its market share and increase its revenue in 2022 and 2023 despite difficulties with lower domestic demand, which had led to companies such as Tyson Foods to look at divesting its China poultry business in 2023. The company is losing share overall and has lost its position as ninth largest company in light of strong losses amounting to USD648 million in 2023.
Post-COVID recovery and health trend lead to the proliferation of new small businesses
The food, beverages and tobacco industry remains largely fragmented, however, unlike industries such as agriculture, the industry is primarily comprised of medium and large-sized companies. In countries such as the UK and Germany, where there are ample innovations in the food and beverages space in light of current difficulties with agricultural production in Europe, and rising consumer demand for healthy products, many new players have entered the market. The post-COVID-19 recovery, coupled with the favourable business conditions in Western markets, has led to the appearance of new small companies, which has further caused fragmentation and proliferation of small and mid-sized companies.
In countries such as Brazil, Canada and South Korea, there is stronger consolidation, due to the presence of strong players in certain categories, such as JBS in processed meat. Similarly, for tobacco, a few large companies dominate the space, which is consolidated due to the legislation and regulations associated with selling such products, as well as the investment needed to develop new alternatives.
China: Slow post-pandemic recovery and low domestic demand hurts the food and beverages industry
Rise of premiumisation in dairy and packaged food in line with rising health concerns
Lower domestic demand and declining population impact the meat sector
China has been experiencing a slow post-pandemic recovery following the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions at the end of 2022. In addition, China struggled with a surge in African swine flu cases in 2022 which coupled with low domestic demand in 2023 due to high consumer price sensitivity has led to producers making strong losses in the first half year of 2023. The low demand has also impacted other meat categories, such as poultry, causing large companies such as Tyson Foods to look at divesting its poultry farming and processing business.
It is expected that demand will slowly start recovering in the second half of 2023, and especially in 2024. However, disruptions in production due to losses are likely to lead to skyrocketing prices, as demand outgrows supply, which is likely to boost internal pork production again, in the meantime relying on supplies from Brazil.
Premiumisation trend driven by rising urbanisation and busy lifestyles following the lifting of COVID-19 measures
Following the lifting of COVID-19 measures and the return to busy lifestyles, there is a growing premiumisation trend towards ready meals, which are driving value sales in the food processing industry. In ready meals, high-end foodservice players and start-ups have joined the market, competing with high-quality ingredients and an experience similar to foodservice.
Amidst a rising middle class and changing diets, more Chinese consumers are looking for quick and convenient meals, as well as looking for exciting and new culinary experiences.
Dairy products benefit from strong government support and premiumisation
As part of a government initiative to boost self-sufficiency, prices of dairy products declined due to excess supply. Manufacturers actively introduced high-end, premium products to enhance their profit margins.
Manufacturers focused on attributes such as high protein content, low- or zero-fat content in milk and sugar-free or clean-label options in yoghurt and and organic milk. On the other hand, private label also performed well as consumers remained price sensitive in light of the uncertain economic situation.
US: Slowing growth in production value due to high costs of production
Commodification of meat and profit losses in the US lead to struggling meat industry
Premiumisation in certain food categories continues despite cost-of-living crisis
The cost-of-living crisis and increasing food inflation have caused US consumers to adopt a frugal mindset and trade down on certain food products, while deciding to splurge on categories considered as affordable luxuries.
The premiumisation trend has been seen in food categories such as high-end frozen pizza, pasta sauce, healthy refrigerated meals and snacks, as consumers are looking for convenience and novelty, instead of familiarity, in order to justify product value. The willingness to spend more for such categories is also seen in light of consumers deciding to cut their spending on eating outside and looking for higher-end alternatives at home.
Commodification of meat amidst companies losing profits
In 2023, the processed meat category has faced challenges which are expected to continue ahead, amidst a process of commodification in terms of pricing. Key food players such as Tyson Foods reported losses in 2023, in addition to JBS which reported a net loss of over USD50 million in 2023.
Companies have had to readjust their profit margins, despite raising prices, due to the prevalence of private label which has pushed meat commodification and has caused players to reduce their prices in order to compete, amidst slowing meat production and the cost-of-living crisis.
Plant-based dairy performing well amidst health and wellness trend and stagnating dairy industry
The dairy industry has faced challenges due to high costs, droughts, decreased production, labour shortages and smaller players exiting the market. On the other hand, plant-based milk has seen strong performance in 2023, in light of the ongoing health and wellness trend. The price gap between the two options has decreased in 2023, as producers have scaled up plant-based production and investment.
Continuous innovation, increased nutritional value of plant-based milk through more blends and functional ingredients added and rising health concerns are likely to boost the value of this sector in 2023 and 2024 and provide growth opportunities.
Key findings
High costs still weigh on producers despite inflation slowdown in 2023
Despite an inflation slowdown in 2023, manufacturers are still impacted by the lagging effects of the uncertain economic conditions since the start of the pandemic, and especially in 2022. High energy prices, ongoing labour shortages, increase in the price of raw materials and sluggish demand due to the cost-of-living crisis have led to many companies exiting the industry, or moving to mergers and acquisitions and consolidation in order to weather the situation.
Health and wellness trends continue to drive innovation and attract consumer demand
The challenging situation during the pandemic has also opened many doors and opportunities for manufacturers to respond to rising health and environmental concerns, increase the value of their production and drive innovation. In Western countries, there has been an increase in the number of start-ups and companies looking at using technologies to increase the quality and functionality of food, beverages and tobacco products.
Geopolitical tensions lead to supply chain changes and shifting trade patterns
Rising geopolitical tensions stemming from the war in Ukraine and deteriorating relations between China and the West have caused a rearrangement of supply chains, with Russia and China turning to alternative countries in order to source their supply, decrease their reliance on Western countries, as well as boost their domestic production. This change in trade patterns has boosted the competitive advantage of countries such as Brazil and India.
Developing countries are boosting investment and government support towards food and beverage processing industries
Developing countries such as India and Indonesia are increasingly investing in their food and beverages processing capacity in order to boost their self-sufficiency, as well as increase the value of their production. With an abundance of raw materials, governments are heavily investing in machinery and inputs in order to build their production capacity, and boost the quality and safety of their products, in order to make them competitive.